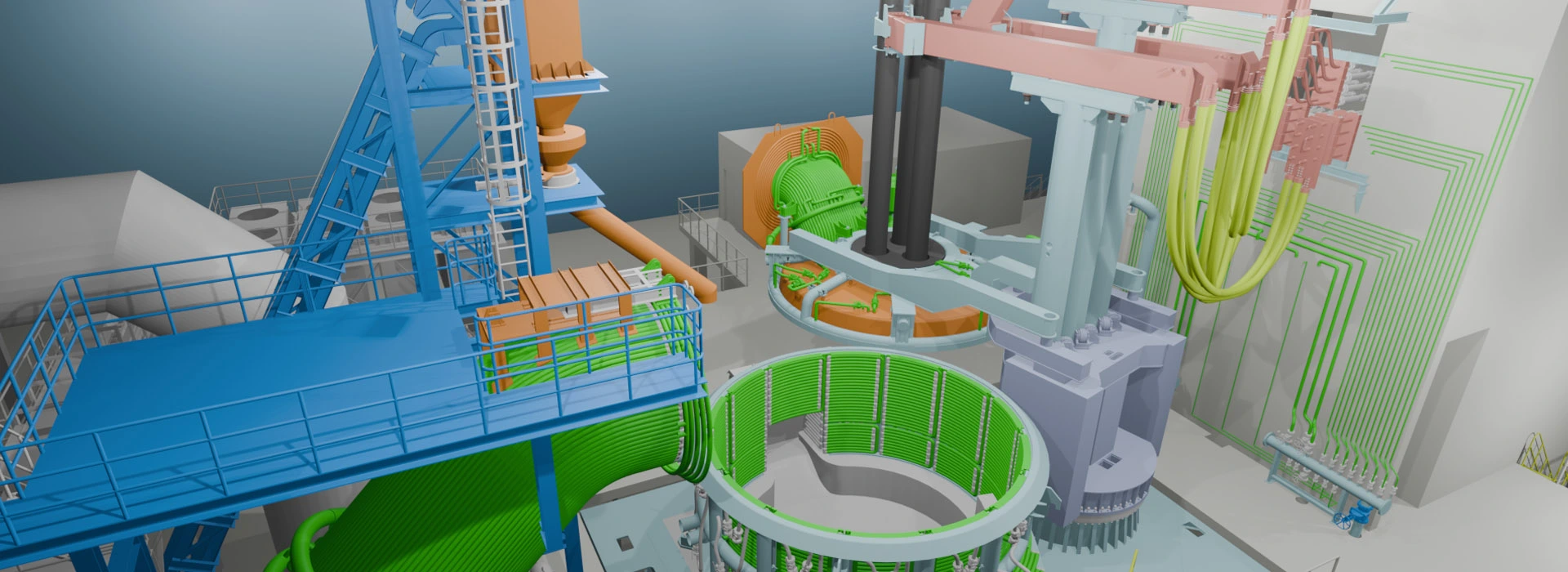
Electric arc furnace steel making is a process that uses electric heating technology to melt and refine iron containing materials such as scrap steel into steel. Electric arc furnace EAF steelmaking occupies a dominant position in the production of special steel with small batches, multiple varieties, and high alloy ratios. CHNZBTECH, one of the leading steel furnace manufacturers, offers steelmaking EAF electric arc furnace with following advantages.
1. Environmental advantages: Electric arc furnace steel making can fully utilize the abundant domestic scrap steel resources, reduce raw material costs and environmental pollution.
2. Flexibility: Among types of steel making furnaces, electric furnace can achieve miniaturization, flexible production, and rapid adjustment to adapt to changes in market demand.
3. Technical advantages: In the electric arc furnace steel making process, the power input can be precisely controlled, and key parameters such as melting speed, smelting temperature, and furnace atmosphere can also be effectively controlled.
4. Economic advantages: Electric arc furnace steel making has low energy consumption, short construction period, and simple operation, resulting in low operating costs and strong adaptability.
 back homepage
back homepage
 EN
EN
 fr
fr  ar
ar  fa
fa